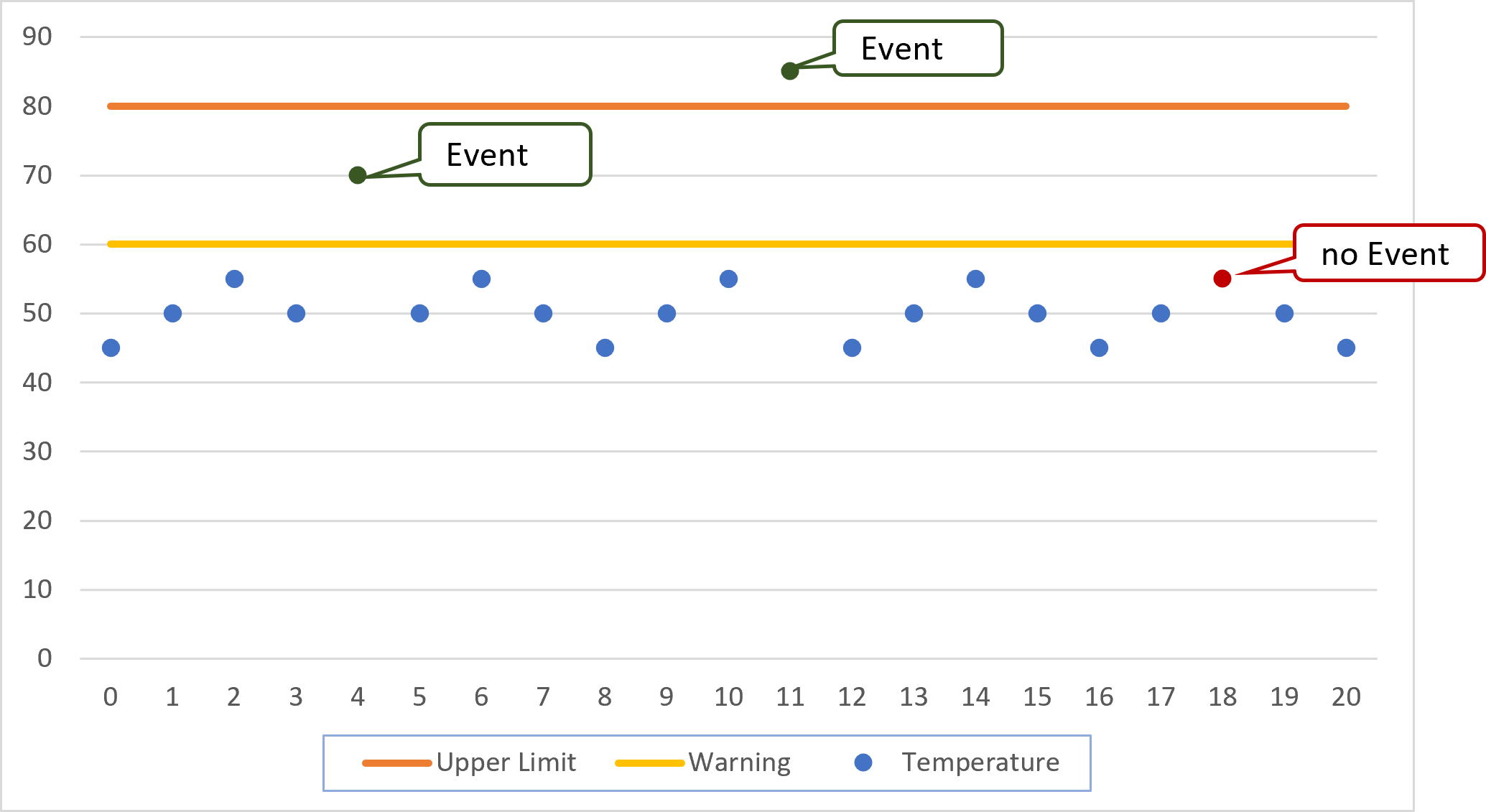
The Upper Limit (Calculated Limit) and Lower Limit (Calculated Limit) rule types first check whether the most recent measured value including the deviation is above or below the configured limit value (80 and 20 in this example). The system then checks whether the measured value is above or below the configured warning limit. This warning limit can be defined with Absolute or Relative Values.
The PPMP upper/lower limit error is also included in the calculation. If the most recent measured value is above or below the limit value, the previous measured values are checked. The event is triggered when a set number of measured values exceeds or undershoots the configured limit.
Calculation of limit values:
Upper limit of the warning limit: Upper limit – deviation
Lower limit of the warning limit: Lower limit + deviation
Upper limit of the warning limit: Upper limit – (upper limit*relative deviation/100)
Lower limit of the warning limit: Lower limit + (lower limit*relative deviation/100)
Upper limit of the warning limit: Upper limit – (relative deviation/100 * ((upper limit – lower limit)/2))
Lower limit of the warning limit: Lower limit + (relative deviation/100 * ((upper limit – lower limit)/2))
Rule type variants
Example
In the machine data, the upper temperature limit is set to 80°C. A warning is to be issued if the temperature is 20°C away from the upper limit.
If the measured value exceeds 60°C, an event is triggered.
